What is Transmission media?
- Transmission media is a communication channel that carries the information from the sender to the receiver. Data is transmitted through the electromagnetic signals.
- The main functionality of the transmission media is to carry the information in the form of bits through LAN(Local Area Network).
- It is a physical path between transmitter and receiver in data communication.
- In a copper-based network, the bits in the form of electrical signals.
- In a fibre based network, the bits in the form of light pulses.
- In OSI(Open System Interconnection) phase, transmission media supports the Layer 1. Therefore, it is considered to be as a Layer 1 component.
- The electrical signals can be sent through the copper wire, fibre optics, atmosphere, water, and vacuum.
- The characteristics and quality of data transmission are determined by the characteristics of medium and signal.
- Transmission media is of two types are wired media and wireless media. In wired media, medium characteristics are more important whereas, in wireless media, signal characteristics are more important.
- Different transmission media have different properties such as bandwidth, delay, cost and ease of installation and maintenance.
- The transmission media is available in the lowest layer of the OSI reference model, i.e., Physical layer.
Some factors need to be considered for designing the transmission media:
- Bandwidth: All the factors are remaining constant, the greater the bandwidth of a medium, the higher the data transmission rate of a signal.
- Transmission impairment: When the received signal is not identical to the transmitted one due to the transmission impairment. The quality of the signals will get destroyed due to transmission impairment.
- Interference: An interference is defined as the process of disrupting a signal when it travels over a communication medium on the addition of some unwanted signal.
Causes Of Transmission Impairment:
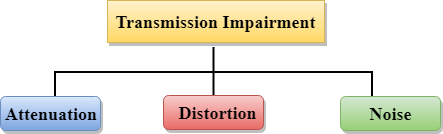
- Attenuation: Attenuation means the loss of energy, i.e., the strength of the signal decreases with increasing the distance which causes the loss of energy.
- Distortion: Distortion occurs when there is a change in the shape of the signal. This type of distortion is examined from different signals having different frequencies. Each frequency component has its own propagation speed, so they reach at a different time which leads to the delay distortion.
- Noise: When data is travelled over a transmission medium, some unwanted signal is added to it which creates the noise.
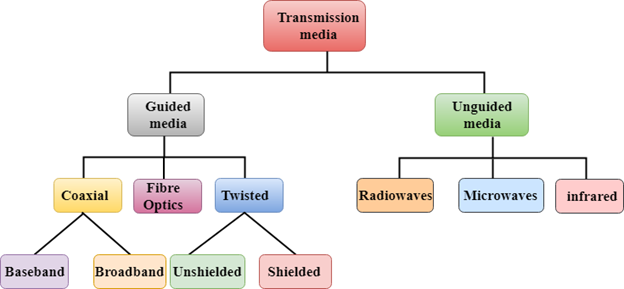
Classification Of Transmission Media:
Comments
Post a Comment